Blog
Up-Leveling Your Workout Game, but Muscle Cramps Keep Getting in the Way?
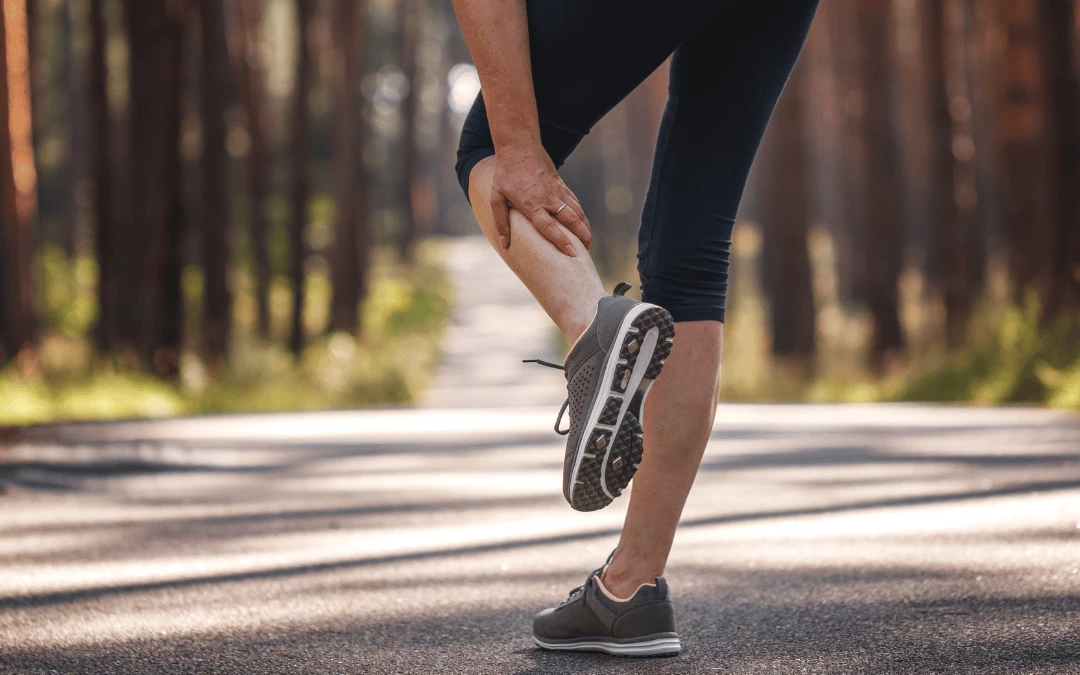

Have you ever experienced that sudden muscle squeeze or pulling sensation that halts your progress, whether you're out for a run or getting comfortable in bed? Those are muscle cramps.
Muscle cramps can appear as unwelcome guests at any time of the day or night. During the day, they can disrupt your workouts or even simple tasks, unnecessarily making things more difficult. And just when you think you're safe in dreamland, bam!—cramps while sleeping can jolt you awake, leaving you puzzled.
Whether you're in the midst of a jog or peacefully drifting off, muscle cramps have a knack for surprising you. But why do they occur?
Let's uncover the mystery behind these unexpected muscle cramps and explore ways to minimise their presence in our daily and nightly routines.
Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps occur when muscles contract suddenly and involuntarily. They can cause pain and affect various muscle groups. 1,2
The most commonly affected muscles are located in the back of the lower leg, the back of the thigh, and the front of the thigh. 1
Cramps can cause intense pain, making it challenging to walk or engage in activities. The sharp pain may last for a few seconds to 15 minutes.

Causes of Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps can occur for various reasons. Overusing your muscles, especially while exercising, can cause cramps.1 Heat can also result in cramping, which is a common issue in hot weather conditions like Malaysia during sports or other rigorous physical activities.2
Excessive sweating not only results in water loss but also depletes important minerals known as electrolytes. These electrolytes, including magnesium, sodium, and potassium, are essential for proper muscle function. The loss of electrolytes can cause muscles to contract involuntarily and lead to cramping.1,3
Another potential cause of muscle cramp is a lack of magnesium in the diet or excessive magnesium loss due to certain health conditions or the use of specific medications.4

Muscle Cramps Treatment
Muscle cramps can be relieved by using a hot or cold compressor stretching as soon as spasms are felt.1 Ensuring proper hydration by drinking plenty of water is important in maintaining electrolyte balance and reducing the risk of muscle cramps.2
For persistent muscle cramps, trying a magnesium supplement can be beneficial in alleviating the pain caused by these spasms.
Crushing Muscle Cramps with Magnesium
Magnesium is essential for proper muscle function, aiding in both muscle contraction and relaxation.5 Magnesium works alongside other electrolytes such as potassium and calcium, to maintain the balance of ions within cells, which is crucial for normal muscle function.5 However, imbalances in these electrolytes can lead to cramps and spasms.
A 2020 study revealed that individuals who took 300 mg of magnesium daily for 6 weeks experienced fewer muscle cramps compared to those who received a placebo.5 Based on this finding, incorporating a daily dose of magnesium could be an effective approach to combat muscle cramps.
Kordel’s Magnesium Amino Acid Chelate 750 is highly effective in relieving muscle cramps and stiffness. It is formulated to be in a chelated form of magnesium which is easily absorbed into the body compared to other forms.
Simply take 1 capsule twice daily with your meals and experience the noticeable difference it makes!

Enhance Your Workout Game with Magnesium
Magnesium has also been found to improve exercise performance, taking your game to the next level! Studies have shown that magnesium enhances the absorption of blood sugar in muscle cells and reduces the buildup of lactate during exercise, which is the major contributor to muscle soreness and fatigue.6,7 This provides your muscles with the energy needed for efficient energy metabolism during your workout, allowing you to push yourself further.
In a 2019 study, male cyclists who took a daily dose of 400 mg of magnesium for three weeks experienced improved muscle recovery and protection from muscle damage after a race, compared to those who took a placebo.8 Another study involving 2570 women with higher magnesium intake found increased muscle mass and power.9
The evidence from these studies highlights the important role that magnesium plays in improving exercise performance.
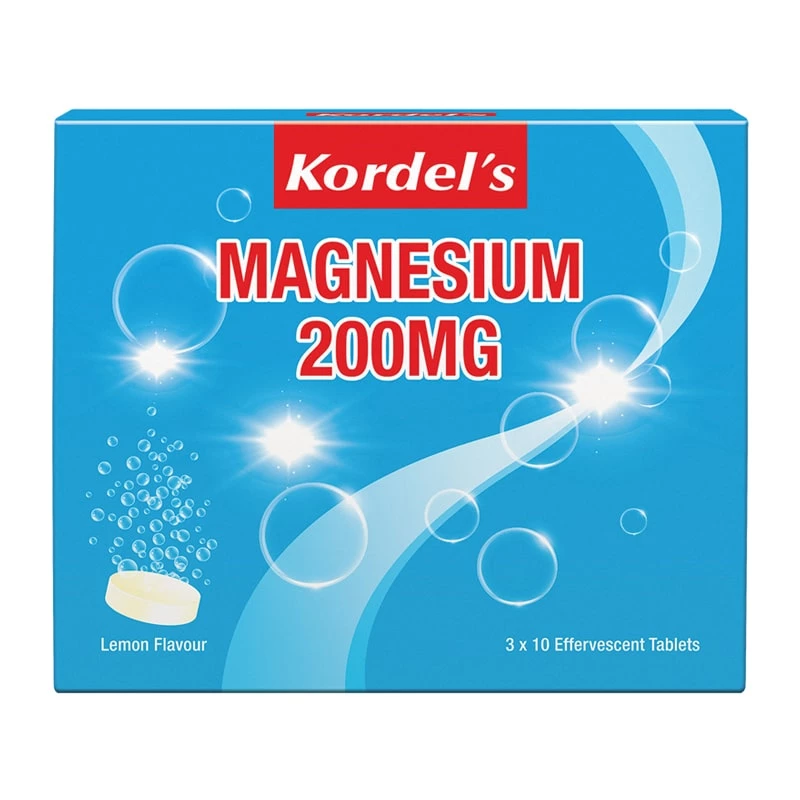
Not a fan of swallowing pills? No worries! Try Kordel’s Magnesium 200mg Effervescent for a refreshing alternative. It's not just a good choice; it's an excellent one made for you! Simply dissolve 1 effervescent tablet in 100 – 150ml of water before or after a workout and feel the power! It provides effortless relief in a fizz.
Benefits of Kordel’s Magnesium:
- Boosts energy production
- Improves muscle strength
- Supports post-workout muscle recovery
- Reduces muscle cramps and soreness
Say goodbye to muscle cramps and stiffness and hello to unlocking your best workout with Kordel’s Magnesium!
References
- Higuera, V. (2019). What Causes Muscle Cramps? Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/muscle-cramps#causes
- Bordoni B, Sugumar K, Varacallo M. Muscle Cramps. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499895/
- J. Hoenderop, J. G., & M. Bindels, R. J. (2014). Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiological Reviews. https://doi.org/PRV-00012-2014
- Office of Dietary Supplements - Magnesium. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/#h8
- Garrison SR, Korownyk CS, Kolber MR, Allan GM, Musini VM, Sekhon RK, Dugré N. Magnesium for skeletal muscle cramps. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 9. Art. No.: CD009402. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009402.pub3. Accessed 24 November 2023.
- Chen HY, Cheng FC, Pan HC, Hsu JC, Wang MF. Magnesium Enhances Exercise Performance via Increasing Glucose Availability in the Blood, Muscle, and Brain during Exercise. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e85486.
- Zhang, Y., Xun, P., Wang, R., Mao, L., & He, K. (2017). Can Magnesium Enhance Exercise Performance? Nutrients, 9(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9090946
- Setaro L, Santos-Silva PR, Nakano EY, Sales CH, Nunes N, Greve JM, Colli C. Magnesium status and the physical performance of volleyball players: effects of magnesium supplementation. J Sports Sci. 2014;32(5):438-45. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2013.828847. Epub 2013 Sep 9. PMID: 24015935.
- Welch AA, Kelaiditi E, Jennings A, Steves CJ, Spector TD, MacGregor A. Dietary Magnesium Is Positively Associated With Skeletal Muscle Power and Indices of Muscle Mass and May Attenuate the Association Between Circulating C-Reactive Protein and Muscle Mass in Women. J Bone Miner Res. 2016 Feb;31(2):317-25. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2692. Epub 2015 Sep 11. PMID: 26288012.
If you like this, click to show us your support




Blog Comments